By: SV-1
Maybe this will help convince some people that they're not gonna die if they don't bake the sh*t out of their juice. Concentrate on clean conditions, proper technique, use a good filter (.2 micron) and you should be fine.
Development of a Multidose Formulation for a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Using Experimental Design Techniques
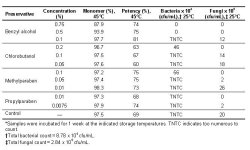
"The efficacy of the preservative against various microorganisms was measured using a modified USP/EP PET (referred to as preservative screening test in this document). Tests were conducted at Microconsult Inc (Dallas, TX). In the procedure, formulations were tested against the following microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus niger. The 3 bacterial strains were inoculated together at a total concentration of ~105 cfu/mL, as were the 2 fungi. Samples were incubated for 7 days at room temperature (25°C), and the total bacterial and fungal counts were measured using a colony counter. The log reduction (LR) values for the bacterial and fungal counts were calculated as log (initial count/final count)."
"Results of the preservative screening tests showed that the formulations containing 0.75% and 0.5% benzyl alcohol are potential candidates to meet the USP/EP criteria (Table 4). Both formulations demonstrated a complete kill of the tested bacterial and fungal species after 7 days. For all other samples, either the total bacterial count after 7 days was too numerous to count, or no effective reduction in the bacterial count was observed."
"Benzyl alcohol caused significant aggregation at high concentrations (≥1.0%); however, it was the most effective preservative in maintaining antimicrobial efficacy against bacteria and fungi."
Maybe this will help convince some people that they're not gonna die if they don't bake the sh*t out of their juice. Concentrate on clean conditions, proper technique, use a good filter (.2 micron) and you should be fine.
Development of a Multidose Formulation for a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Using Experimental Design Techniques
"The efficacy of the preservative against various microorganisms was measured using a modified USP/EP PET (referred to as preservative screening test in this document). Tests were conducted at Microconsult Inc (Dallas, TX). In the procedure, formulations were tested against the following microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus niger. The 3 bacterial strains were inoculated together at a total concentration of ~105 cfu/mL, as were the 2 fungi. Samples were incubated for 7 days at room temperature (25°C), and the total bacterial and fungal counts were measured using a colony counter. The log reduction (LR) values for the bacterial and fungal counts were calculated as log (initial count/final count)."
"Results of the preservative screening tests showed that the formulations containing 0.75% and 0.5% benzyl alcohol are potential candidates to meet the USP/EP criteria (Table 4). Both formulations demonstrated a complete kill of the tested bacterial and fungal species after 7 days. For all other samples, either the total bacterial count after 7 days was too numerous to count, or no effective reduction in the bacterial count was observed."
"Benzyl alcohol caused significant aggregation at high concentrations (≥1.0%); however, it was the most effective preservative in maintaining antimicrobial efficacy against bacteria and fungi."